Human DNA
All nucleic acids are polynucleotides. A nucleotide consists of three components:
1. A nitrogenous base: (Adenosine and guanine which are based on purine rings, Thymine and cytosine which are based on pyrimidine rings).
2. A pentose sugar (deoxyribose in DNA and Ribose in RNA) at 3′ end
3. 1-3 phosphate groups at 5′ end
There are two kinds of nucleic acids:
o Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
o Ribonucleic acid (RNA).
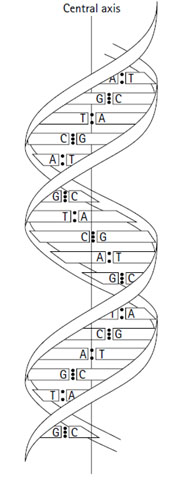
•Two polynucleotide chains are linear but antiparallel (i.e. one chain runs in a 5' to 3' direction; the other runs 3' to 5').
• The sugar and phosphate groups form the linear backbone of the strands with the bases projecting inwards towards their partners held together by hydrogen bonds between the opposing bases:
ü Adenine (A) pairs only with thymidine (T) (2 hydrogen bonds)
ü Guanine (G) pairs only with cytosine (C) (3
hydrogen bonds).
· Multiple fragments that, together with a protein skeleton (chromatin), form chromosomes.
· Site: Nucleus and Mitochondria.